Teamcenter Active Workspace (AWC) is Siemens’ modern web platform that allows users to access PLM data from any device using only a browser. While it looks simple on the front end, the architecture behind AWC is made of several layers that work together to deliver fast, secure, and scalable PLM capabilities.
To make the structure easy to understand, imagine AWC as a series of layers stacked on top of each other. Each layer has a specific job and passes information to the next one.
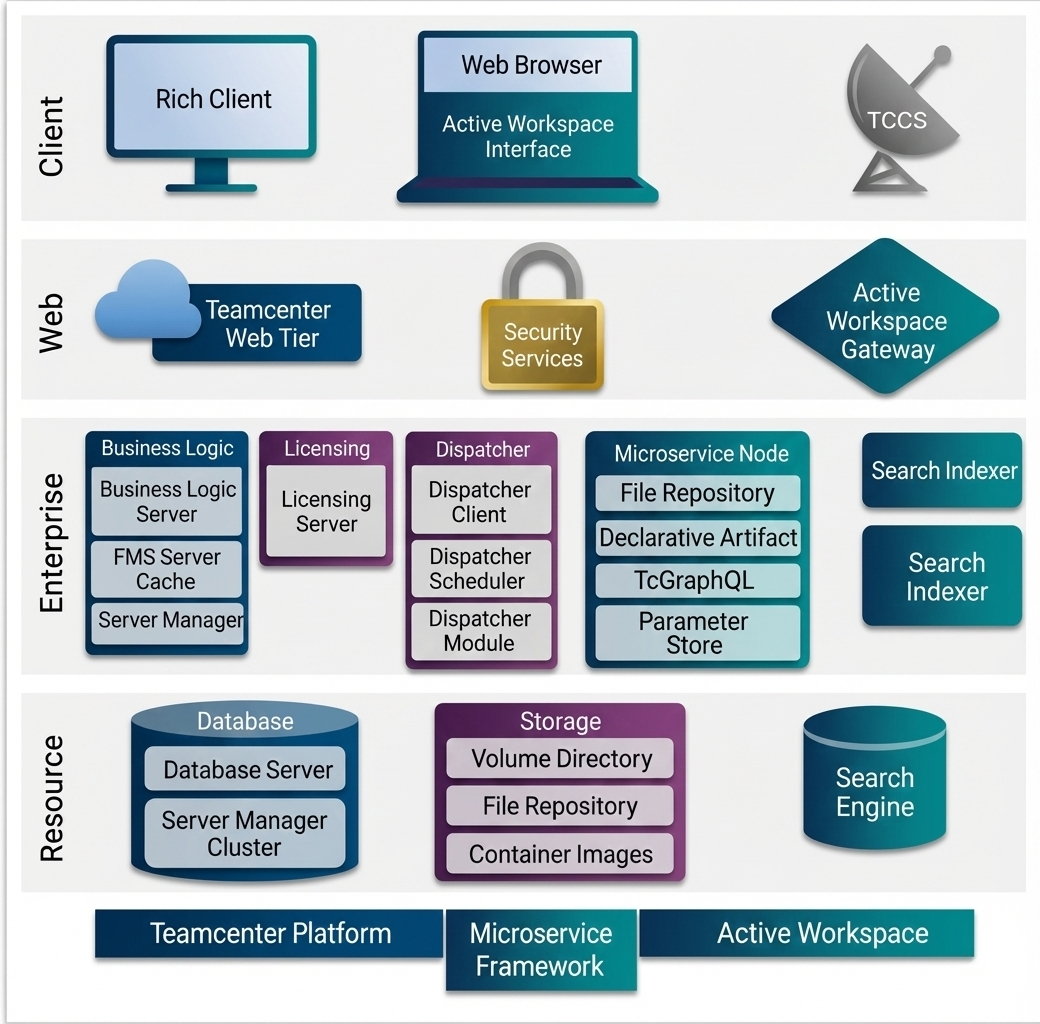
Client Layer — Where Users Interact
The topmost layer is where users interact with Teamcenter. There are two major clients:
Rich Client
This is the installed desktop application traditionally used by engineers and administrators. It offers deep functionality and is suitable for power-users who need advanced features.
Active Workspace (Web Browser)
This is the lightweight, browser-based interface. It requires no installation and is easier for occasional users, managers, suppliers, and shop-floor workers. AWC communicates with Teamcenter through web services, making it faster and more intuitive.
Both clients ultimately talk to the same Teamcenter backend, but AWC does it through modern web protocols.
Web Layer — The Middle Layer that Manages Requests
When a user performs an action in AWC (like opening an item or searching), the request is sent to the web layer.
Teamcenter Web Tier
This tier receives requests from the browser and translates them into calls that the Teamcenter servers can understand. It handles:
-
- User sessions
- Packaging data
- Communication between clients and enterprise services
Security Services
Security Services act as the gatekeeper. They verify who is logging in, check permissions, and ensure data is passed securely. This includes SSO (Single Sign-On), token handling, user authentication, and access validations.
Active Workspace Gateway
This gateway optimizes communication between the browser and the microservices. It also manages authentication, routing, and performance-related functions. It ensures that AWC loads content quickly and efficiently.
Enterprise Layer — The Brains of Teamcenter
This is where most of the business logic, rules, and heavy operations are performed. It includes several major components:
Business Logic Services
These services process user requests such as opening a BOM, retrieving part data, performing lifecycle operations, or validating workflows. They communicate with the FMS (File Management System) for file-related data.
Licensing Services
These ensure that the user has the correct license to perform an operation. Teamcenter checks licenses dynamically, allowing organizations to manage software usage efficiently.
Dispatcher Services
Dispatchers handle background processing, such as:
-
- Translation of files (JT, PDF, DXF, STEP, etc.)
- Generating thumbnails for AWC
- Handling format conversions
- Managing translation queues
The Dispatcher Scheduler manages queued jobs, while the Dispatcher Client executes each task.
Microservice Node
Newer Teamcenter versions introduce microservices to offload certain activities from the main server. These services are lightweight, individually deployable, and improve performance.
Common microservices include:
-
-
File Repository
-
Declarative Artifacts
-
GraphQL-based queries (TcGraphQL)
-
Parameter Store
-
These microservices allow AWC to fetch data faster and in a more optimized format.
Visualization Server
This server handles visualization-related activities, such as rendering JT files, assigning pool resources, and serving visualization content. It is essential for 3D viewing inside AWC.
Resource Layer — The Foundation of the System
This is the bottommost layer and forms the “data foundation” of Teamcenter.
Database Server
All PLM objects—items, BOMs, workflows, metadata—are stored here. The database cluster ensures reliability and high availability.
Storage System
This contains file data such as:
-
- Volume directories
- File repositories
- Container images
This layer works with the File Management System to store and retrieve CAD files, PDFs, JT files, and other datasets.
Search Engine
Teamcenter uses a dedicated search engine for fast indexing and retrieval. This enables AWC’s quick search capabilities and filtering functions.
To Summarize ,Active Workspace provides a clean and easy interface, while Teamcenter’s Layers work in the background to ensure secure, fast and reliable access to all PLM data.
Engineering Usage of Active Workspace
Active Workspace is extensively used by engineering teams due to its capability to streamline daily PLM and CAD activities.
Common Engineering Use Cases
-
Browse and manage Items, BOMs, Change Requests, and workflows.
-
Access CAD data directly in the browser.
-
Launch CAD applications with TCCS.
-
Perform 3D/2D visualization using JT viewer.
-
Participate in engineering workflows such as:
- Design Release
- Change Management
- Review and approval cycles
-
Perform BOM comparisons and configurations.
-
Execute MPP/MRL operations in manufacturing environments.
Why Engineers Prefer AWC
-
Fast UI with personalized dashboards.
-
3D visualization without installing separate viewers.
-
Reduce dependency on high-end workstation hardware.
-
Seamless collaboration across design, manufacturing, and quality teams.
Benefits of AWC vs Teamcenter 2-Tier and 4-Tier RAC
Zero Install vs Heavy Desktop Client
-
-
- AWC: Runs in a browser. No installation needed.
- RAC: Large client package with complex update cycles.
-
Faster Upgrades
-
-
- AWC: UI updates deployed at server level → instant for users.
- RAC: Requires packaging and reinstalling client updates.
-
Better Performance via GraphQL + Microservices
-
-
- AWC: Uses modern GraphQL queries, microservices, and optimized caching.
- 2-Tier/4-Tier: Legacy SOA-heavy communication, more data load, slower for remote users.
-
Cloud-Ready Architecture
-
-
- AWC: Designed for on-cloud/hybrid deployments with microservices.
- RAC: Traditional architecture, not suited for cloud scaling.
-
Lightweight Visualization
-
-
- AWC: In-browser JT viewer with multi-CAD visualization.
- RAC: Requires standalone visualization tools or plug-ins.
-
Better UX & Mobile Access
-
- AWC: Modern and intuitive, accessible on tablets and mobiles.
- RAC: Not mobile-friendly.
Lower Total Cost of Ownership
-
- Less IT overhead
- Reduced client support effort
- Simplified deployment pipeline
==================================================================================================================================================
What’s Next? We have more deep dives into PLM Tutorials, Teamcenter, and Active Workspace coming your way soon.
We value your feedback! Please share your thoughts in the comment section below.
If you have specific technical questions, feel free to post them in our Forum via the “Add Topics” button, and our team will provide a solution as soon as possible.

Stay Connected:
Follow us on our social media platforms for the latest updates, or reach out with suggestion at [email protected].


